Advantages of Virtual Reality (VR)
Posted on September 13, 2023 20 minutes 4222 words
Table of contents
Introduction
1. Brief History of VR
The concept of virtual reality (VR), the immersive, three-dimensional environment, has roots tracing back to the 1960s, although glimpses of the idea can be found much earlier in science fiction literature and panoramic paintings.
- 1950s to 1960s:
- Sensorama (1956): Morton Heilig, a cinematographer, conceptualized and later built the Sensorama in 1962, which is considered one of the earliest examples of VR technology. This device was a standalone machine that featured stereo speakers, a stereoscopic 3D display, fans, and even a scent producer to immerse the user fully.
- The Sword of Damocles (1968): Ivan Sutherland created the first head-mounted display (HMD), dubbed “The Sword of Damocles,” laying a foundational stone in VR technology.
- 1970s to 1980s:
- During this period, developments were relatively slow but steady, with various sectors like the military starting to explore the use of VR for simulation training.
- 1990s:
- The 90s marked a significant period for VR, with technology companies like Sega and Nintendo dabbling in the VR space. Products such as Sega VR and Nintendo’s Virtual Boy were released but didn’t gain much commercial success.
- Virtual Reality Modelling Language (VRML): In 1994, VRML was developed to create 3D interactive vector graphics on the internet, showcasing the potential for VR in web browsers.
- 2000s:
- This era witnessed the resurgence of VR, primarily driven by advancements in technology and graphics. Companies started investing more in developing VR products, although it remained quite niche.
- 2010s to Present:
- Oculus Rift (2012): The announcement and later release of the Oculus Rift marked a significant milestone in making VR technology more accessible and popular to the general public.
- Further Developments: Other major tech players, like Sony with PlayStation VR and HTC with Vive, joined the fray, enhancing the technology and reducing the cost to make it more accessible to consumers.
2. Current Trends
In recent years, VR technology has seen exponential growth and adoption across various industries. Let’s explore some of the prevalent trends that are shaping the VR landscape:
- Integration with Augmented Reality (AR): Companies are increasingly blending Virtual Reality (VR) with Augmented Reality (AR) to create mixed reality experiences that offer even more immersive and interactive environments.
- Wireless Technology: The newest VR headsets are incorporating wireless technology, allowing for more freedom of movement and a more immersive experience.
- Haptic Feedback: Developers are incorporating haptic feedback into VR systems to enhance the sensory experience, making virtual environments feel more real by stimulating the sense of touch.
- Social VR: Social VR platforms are on the rise, allowing users to interact with each other in virtual spaces, fostering new forms of socialization and collaboration.
- Use in Telemedicine: The healthcare sector is utilizing VR for telemedicine, offering remote consultations and therapies, particularly accentuated due to the COVID-19 pandemic.
- Educational Applications: VR is being adopted in education at a rapid pace, providing immersive learning experiences that can enhance understanding and retention of knowledge.
- Real Estate and Architecture: VR technology is being used extensively in the real estate and architecture sectors for virtual tours, allowing clients to explore properties and designs from anywhere in the world.
- Content Creation: With the democratization of VR technology, there has been a surge in VR content creation, with various platforms offering tools to create and share VR content.
By examining the journey of VR from its inception to its current state, it is evident that the technology has not only matured significantly but has also found applications in diverse fields, enriching experiences and opening new avenues for innovation and growth. The future of VR promises even more advancements, as it continues to redefine the boundaries of interaction, communication, and visualization.

1. Immersive Learning Experiences
1.1 Education and Training
Virtual Reality (VR) has revolutionized the educational sector by offering hands-on, immersive learning experiences that significantly enhance both the understanding and retention of information. Here’s how it works:
- Interactive 3D Models: VR allows students to interact with 3D models of objects, which can be particularly beneficial for understanding complex concepts in subjects such as biology, astronomy, and chemistry. These interactive 3D models can provide students with different perspectives, allowing them to explore the inner workings of a molecule or the structure of a solar system, for instance.
- Virtual Field Trips: Through VR, students can undertake virtual field trips to historical sites, museums, and geographical locations that would be logistically challenging and expensive to visit in real life. This not only broadens their horizons but also provides a richer context and depth to their learning experiences.
- Safe Environment for Skill Development: VR offers a safe environment where students can learn and hone their skills without the risk of real-world consequences. This is especially beneficial in vocational training programs where students can practice and make mistakes without any repercussions, encouraging a trial-and-error learning approach.
- Customized Learning Paths: VR supports personalized learning by allowing educators to customize content to suit individual learning styles and paces. This helps in creating a more inclusive learning environment where each student can thrive.

1.2 Language Learning
Language learning through VR is a transformative experience, as it facilitates immersion, which is a key aspect in picking up a new language effectively. Here are the ways VR aids language learning:
- Virtual Immersion: Through VR, learners can immerse themselves in environments where the target language is natively spoken. This virtual immersion helps in enhancing their language comprehension skills and provides them with a nuanced understanding of the language, including the cultural contexts in which it is used.
- Interactive Conversations: VR platforms can simulate conversations with native speakers, providing learners with an opportunity to practice their speaking and listening skills in realistic scenarios. This kind of interactive learning can be far more engaging and effective compared to traditional methods.
- Language Games: Language learning can be made more enjoyable through VR-based language games that encourage learners to apply their language skills in fun and interactive ways, which can help in better retention of new words and grammatical structures.
1.3 Medical Training
In the medical field, VR serves as a potent tool for training students and professionals alike, enabling them to practice surgeries and other procedures in a risk-free, controlled, and immersive environment. Here’s how it impacts medical training:
- Surgical Simulations: VR enables medical students to practice surgical procedures through realistic simulations. This allows them to develop their skills, build confidence, and reduce the likelihood of errors when they transition to real-life operations.
- Virtual Cadavers: Medical students can dissect virtual cadavers, providing them with an opportunity to explore the human anatomy in detail without the need for real bodies. This can be especially beneficial in regions where access to cadavers is limited.
- Clinical Skills Development: Beyond surgeries, VR can be used to develop various clinical skills, such as patient communication, diagnostics, and emergency response management. Through VR simulations, students can be exposed to a wide range of clinical scenarios, helping them to be better prepared for real-life situations.
- Continued Professional Development: For experienced healthcare professionals, VR serves as a tool for continued professional development, allowing them to keep up with the latest advancements in medical procedures and technologies, and to practice new skills in a safe environment.
In conclusion, VR technology stands as a beacon of innovation in the education sector, facilitating immersive learning experiences that are both engaging and effective. From general education to specialized training programs, VR has the potential to reshape the learning landscape, making it more interactive, inclusive, and empowering.

2. Enhanced Entertainment
2.1 Gaming
Virtual Reality (VR) has transformed the gaming landscape profoundly by catapulting the gaming experience from two-dimensional screens into immersive three-dimensional environments where players can interact with the virtual world more naturally. Here’s a deeper look at this revolution:
- Immersive Experience: VR transports gamers into vivid, three-dimensional worlds, offering a depth of immersion that surpasses any other gaming format. Players are not just controlling characters but becoming a part of the game themselves, navigating and interacting with the environment in real-time.
- Realistic Graphics and Physics: VR games boast of highly detailed graphics and realistic physics, providing a sensory experience that closely mirrors real life. The intricate detail and realism pull players further into the story, enhancing engagement and excitement.
- Full-Body Gaming: With the integration of motion sensors and haptic feedback, VR gaming has evolved into a full-body experience. Players can use their bodies to perform actions in the game, encouraging physical activity and offering a more dynamic gaming experience.
- Social Connection: VR has introduced new dimensions of social interaction in gaming. Players can connect with friends or other gamers globally in a more intimate and realistic manner, fostering community engagement and collaboration within virtual environments.
- Expanded Genres and Narratives: The VR platform has encouraged innovation in gaming narratives and genres. Developers are experimenting with more complex, non-linear storylines and creating games that offer deeper, more nuanced experiences.
2.2 Virtual Tours
Virtual tours powered by VR technology have reshaped the way individuals explore the world from the comfort of their homes. Here’s how:
- Global Exploration from Home: Virtual tours have broken geographical barriers, enabling users to explore world landmarks, museums, natural wonders, and even outer space without leaving their homes. This not only makes travel more accessible but also promotes cultural understanding and global connection.
- Educational Opportunities: Virtual tours serve as educational tools, providing individuals with an opportunity to learn about different places, historical events, and cultural phenomena in an immersive manner. This enhances the learning experience, making it more engaging and memorable.
- Customized Experiences: Users have the freedom to tailor their virtual tours according to their interests, spending as much time as they want exploring different areas, and even revisiting places to notice new details, which would not be possible during real-life tours.
- Integration with Augmented Reality (AR): Many virtual tours are now integrating AR technology, providing users with additional information and interactive elements during their tours, enhancing the experience and providing a richer, more informed exploration.
2.3 Movies and Theatre
VR is revolutionizing the movie and theatre industries by offering unparalleled immersive experiences that bring stories to life in a whole new way. Here’s a closer look:
- 360-degree Viewing: VR offers 360-degree films where viewers are placed at the center of the action, able to look around and explore the environment, offering a much more immersive viewing experience compared to traditional 2D films.
- Interactive Storytelling: VR opens up avenues for interactive storytelling, where viewers can influence the direction of the story through their actions. This creates a more personalized and engaging viewing experience, as audiences feel a part of the narrative.
- Immersive Soundscapes: VR integrates spatial audio technology to create immersive soundscapes that complement the visual elements, providing a sensory experience that pulls viewers deeper into the world of the film or play.
- Virtual Reality Theatre: In the sphere of theatre, VR enables the creation of virtual theatres where viewers can watch plays and performances in a 3D space, offering a new dimension to live performances and expanding reach to a global audience.
- Film-making Innovations: For filmmakers, VR offers innovative tools and techniques to craft immersive narratives, encouraging experimentation with new forms of storytelling and artistic expression.
In conclusion, VR technology stands at the forefront of a significant shift in the entertainment industry, offering enriched and immersive experiences in gaming, virtual tours, and movies and theatre. As the technology continues to evolve, it is poised to redefine the boundaries of entertainment, offering audiences more engaging, interactive, and personalized experiences.
3. Business Applications
3.1 Real Estate
Virtual Reality (VR) has been a game-changer in the real estate industry, providing opportunities to streamline processes and offer innovative services. Here’s how it is reshaping the real estate sector:
- Virtual Home Tours: In an industry where visualization plays a critical role, VR stands as a potent tool. It enables potential buyers to undertake virtual tours of properties from anywhere in the world. These 360-degree tours provide a realistic, immersive view of the properties, allowing buyers to explore every nook and cranny without having to visit in person. It not only saves time but also helps in narrowing down choices more effectively.
- Customization and Personalization: VR also allows potential homeowners to customize spaces virtually, experimenting with different interior designs, furnishings, and layouts. This personalization helps buyers to visualize how the property would look once it’s tailored to their preferences, assisting in informed decision-making.
- Remote Property Inspection: For real estate professionals, VR facilitates remote property inspections, enabling them to showcase properties to clients in different geographical locations, expanding their customer base and improving sales opportunities.
- Cost-Effective Marketing: VR serves as a cost-effective marketing tool for real estate firms, enabling them to create engaging, interactive property listings that can attract more potential buyers compared to traditional listings.
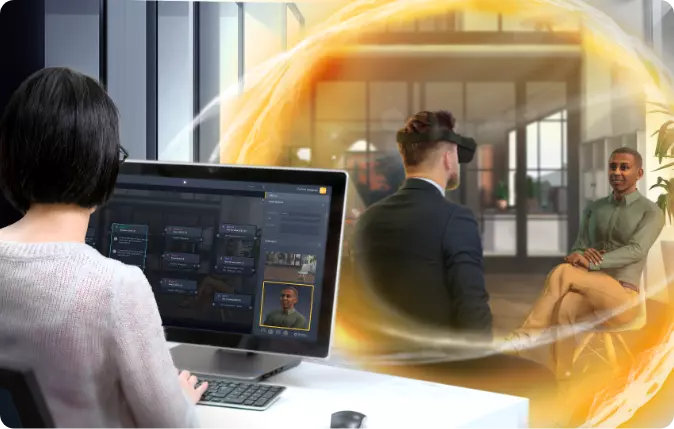

3.2 Product Design and Prototyping
In the realms of product design and prototyping, VR has emerged as an indispensable tool. Here is a detailed analysis of its role:
- Virtual Prototyping: VR allows designers and engineers to create, modify, and test prototypes in a virtual environment before moving to physical production. This not only speeds up the development cycle but also reduces costs associated with physical prototyping.
- Immersive Design Evaluation: Designers can immerse themselves in the virtual environment to evaluate their designs from different perspectives, understanding the spatial and aesthetic aspects more intuitively. This immersive evaluation ensures a more detailed and nuanced design process.
- Collaborative Design: VR facilitates collaborative design processes where teams from various locations can come together in a virtual space to work on the project. This collaborative approach fosters creativity and innovation, allowing for the integration of diverse perspectives and expertise.
- Simulation and Testing: Engineers can use VR to simulate real-world conditions and test how products would perform under different circumstances. This kind of testing provides valuable insights into the product’s functionality and durability, enabling necessary modifications before market release.
3.3 Virtual Conferences and Meetings
Virtual Reality is progressively becoming an essential tool in facilitating virtual conferences and meetings. Here’s how it adds value:
- Engaging Interaction: VR provides a platform where participants can interact in a more engaging manner compared to traditional video conferencing. It creates a virtual meeting space where participants can present, discuss, and collaborate in a more immersive environment, enhancing engagement and communication.
- Virtual Networking: VR enables virtual networking opportunities where participants can meet and interact with peers from around the world, fostering global connections and collaborations, which would be logistically challenging and expensive in a physical setting.
- Enhanced Presentation Capabilities: Presenters can leverage VR to create interactive, 3D presentations that can be explored and manipulated during meetings, offering a more dynamic and impactful presentation experience.
- Training and Workshops: Companies can use VR to conduct training sessions and workshops, providing an interactive learning environment that enhances understanding and retention of information, making training more effective and engaging.
In summary, VR stands as a powerful tool in the business sector, offering innovative solutions and opportunities in real estate, product design, and corporate meetings and conferences. By leveraging VR technology, businesses can streamline processes, enhance engagement, foster innovation, and create more immersive and interactive experiences, setting a new standard for business operations and services.
4. Therapy and Healthcare
Virtual Reality (VR) is progressively establishing itself as an influential tool in therapy and healthcare, enhancing treatment outcomes and revolutionizing patient experiences in several areas. Here is an in-depth exploration of its roles in physical therapy, mental health, and pain management:
4.1 Physical Therapy
VR technology is becoming an essential player in the field of physical therapy, assisting in the rehabilitation of patients who have suffered injuries or surgeries. Here’s how:
- Personalized Rehabilitation Plans: VR allows healthcare providers to create personalized rehabilitation exercises for patients, adapting to their specific needs and progress. This personalization ensures a more focused and efficient recovery process.
- Gamified Exercises: To maintain the motivation levels of patients, VR introduces gamified elements to physical therapy exercises, making them more enjoyable and encouraging consistent participation, which can be crucial for a successful recovery.
- Safe Environment for Therapy: Patients can practice their exercises in a safe and controlled virtual environment, minimizing the risk of further injuries and allowing them to gradually build their confidence and strength.
- Data-Driven Progress Monitoring: VR platforms can track and record detailed data on patients’ performance and progress, providing therapists with valuable insights to adjust treatment plans and optimize outcomes.
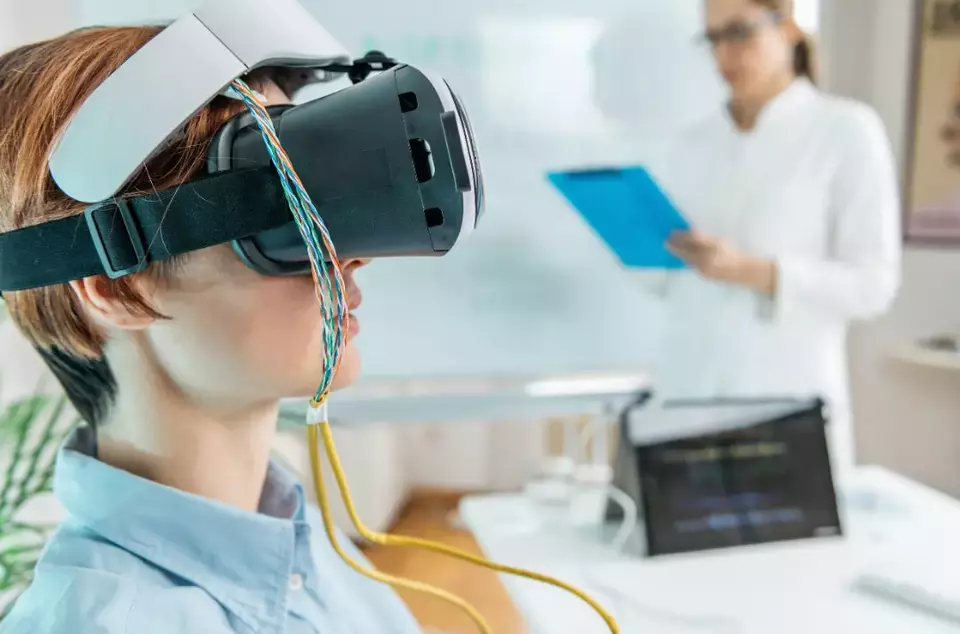

4.2 Mental Health
In the sphere of mental health, VR is paving the way for innovative treatment approaches, particularly in the field of exposure therapy for anxiety disorders and other mental health conditions. Here are the details:
- Controlled Exposure Therapy: VR serves as a powerful tool for exposure therapy, where individuals can confront and deal with their fears and anxieties in a controlled, safe, and private environment. This controlled exposure helps in gradually reducing their anxiety levels and improving their coping mechanisms.
- Immersive Relaxation and Meditation: VR can also offer immersive relaxation and meditation experiences, helping individuals to manage stress and anxiety more effectively. These experiences often incorporate calming visuals and sounds to facilitate deep relaxation.
- Support in Psychotherapy: VR is being used as a complementary tool in psychotherapy, where therapists can leverage VR scenarios to understand their patients’ behaviors and responses better, thus aiding in creating more effective treatment plans.
4.3 Pain Management
VR has shown promising results in the field of pain management, offering innovative approaches to helping patients manage chronic or acute pain. Here’s how:
- Distraction Therapy: VR serves as an effective distraction therapy, where patients can immerse themselves in virtual environments to distract their minds from pain. This immersive distraction has been shown to reduce the perception of pain, particularly during painful medical procedures or chronic pain management.
- Virtual Reality Hypnosis: Some practitioners are exploring virtual reality hypnosis as a method to manage pain. This involves guiding patients into a hypnotic state using VR to modulate pain perception, which can be a beneficial complementary approach in pain management programs.
- Rehabilitation and Mobility Training: In cases where pain is associated with limited mobility, VR can assist in rehabilitation, providing virtual environments where patients can practice mobility exercises in a motivating and engaging way, which helps in reducing pain and improving function over time.
In conclusion, VR technology is unveiling new horizons in the fields of therapy and healthcare, offering innovative approaches to physical therapy, mental health treatment, and pain management. By leveraging the immersive and interactive capabilities of VR, healthcare professionals can enhance treatment outcomes, create engaging therapy experiences, and pave the way for more personalized, effective healthcare solutions.
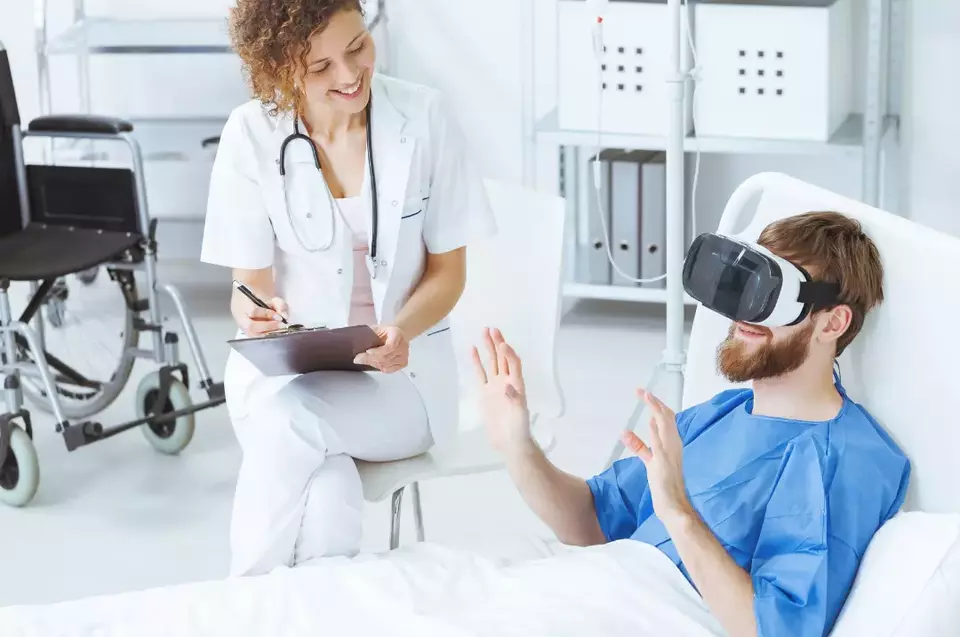

5. Innovation in Various Fields
Virtual Reality (VR) is no longer confined to gaming and entertainment sectors; it is paving the way for groundbreaking innovations in various fields, such as architecture, scientific research, and cultural preservation. Its ability to create immersive, interactive, and visually stunning experiences is proving to be a significant asset in these domains. Here’s an in-depth analysis of how VR is revolutionizing these areas:
5.1 Architecture and Urban Planning
In the fields of architecture and urban planning, VR has emerged as a critical tool that offers myriad benefits, enhancing both the design process and client presentations. Here’s a deeper dive into its influence:
- Virtual Walkthroughs: VR allows architects and planners to create virtual walkthroughs of building designs and urban developments, providing a firsthand experience of the spaces before they are built. These walkthroughs facilitate a deeper understanding of the spatial dynamics and aesthetics, assisting in making informed decisions and adjustments in the design phase.
- Client Engagements: For client presentations, VR takes engagements to a new level. Clients can immerse themselves in the proposed designs, exploring different angles and perspectives, which facilitates a more interactive and satisfying consultation process.
- Collaborative Designing: VR fosters a collaborative environment where teams can work together in a virtual space, sharing ideas and visualizing concepts in real-time. This collaboration not only streamlines the design process but also encourages creativity and innovation.
- Sustainable Urban Planning: In urban planning, VR helps in visualizing and analyzing various environmental and urban factors, assisting planners in creating more sustainable and livable urban developments. Through VR, planners can evaluate the potential impact of new developments on the existing environment, helping to create more informed and responsible urban plans.
5.2 Cultural Preservation
Virtual Reality has found a significant role in the field of cultural preservation, contributing in the following ways:
- Virtual Museums: VR enables the creation of virtual museums where users can explore art, artifacts, and historical exhibits from the comfort of their homes. These virtual experiences offer a new avenue to access and appreciate cultural heritage, reaching a global audience.
- Digital Preservation of Historical Sites: VR is being used to digitally preserve historical sites and monuments, creating virtual replicas that allow users to explore these sites virtually. This digital preservation is crucial in safeguarding cultural heritage against natural disasters, vandalism, or wear and tear over time.
- Interactive Learning: VR offers interactive learning experiences in the field of cultural education, where students and enthusiasts can immerse themselves in historical events, artworks, or architectural wonders, fostering a deeper appreciation and understanding of cultural heritage.
5.3 Scientific Research
Virtual Reality is also making significant strides in the field of scientific research, offering new possibilities and approaches. Here’s how:
- Data Visualization: VR facilitates scientific research by allowing scientists to visualize complex data in three dimensions. This visual representation aids in a more in-depth analysis and understanding of complex phenomena, be it in astronomy, molecular biology, or environmental science.
- Simulated Experiments: VR provides a platform where scientists can conduct simulated experiments in a virtual laboratory, exploring different scenarios and variables without the constraints of a physical setup. This flexibility enables more comprehensive research and experimentation, fostering advancements in various scientific fields.
- Educational Tool: VR serves as an excellent educational tool in science, offering immersive learning experiences where students can explore scientific concepts in a visual and interactive manner, which enhances understanding and retention of complex topics.
In summary, Virtual Reality is at the forefront of fostering innovation in various fields, offering new perspectives and approaches in architecture, scientific research, and cultural preservation. By harnessing the potential of VR, professionals in these fields can create more immersive, interactive, and innovative experiences, advancing their domains to new heights of progress and development.
Conclusion
1. Future Prospects
As we stand on the threshold of a new era where virtual reality (VR) integrates more seamlessly into various aspects of our daily lives, it becomes essential to cast a visionary gaze at the potential future developments within the VR industry.
- Technological Advances: Future iterations of VR are expected to offer even more realistic experiences, backed by significant advancements in graphics, sound technology, and haptic feedback systems. These developments will provide users with an experience that blurs the lines between the virtual and real worlds more effectively.
- Integration with Other Technologies: The convergence of VR with other burgeoning technologies like Artificial Intelligence (AI) and the Internet of Things (IoT) hints at a future where our interaction with the digital environment becomes more intuitive and immersive. This could pave the way for smarter virtual assistants, real-time data analytics, and even more personalized VR experiences.
- Education and Skill Development: The educational sector is set to witness a revolution with VR fostering experiential learning. In the future, we might see virtual classrooms becoming commonplace, with students navigating through historical events or scientific concepts in real time, encouraging a more profound understanding and engagement with the subject matter.
- Virtual Workspaces: As the concept of remote working gains traction, VR could facilitate the creation of virtual workspaces, where teams can collaborate and interact in a more engaging and productive manner, surpassing the limitations posed by traditional video conferencing.
- Healthcare Innovations: The healthcare sector is poised to be a significant beneficiary of VR technology. Future developments might witness VR being used extensively in telemedicine, surgical training, patient therapy, and rehabilitation, augmenting the healthcare delivery systems to be more efficient and patient-friendly.
2. Closing Thoughts
As we retrospect on the multifaceted advantages that VR technology brings to the table, it becomes apparent that we are in the midst of a technological renaissance. The ability of VR to create immersive, interactive, and visually rich environments opens up a plethora of opportunities in various fields, from education to healthcare, business to entertainment.
The power of VR lies in its capacity to transcend geographical and physical barriers, offering experiences that were previously unimaginable. Whether it’s bringing a new dimension to learning, revolutionizing the way businesses operate, or offering therapeutic interventions in healthcare, VR stands as a testament to human ingenuity and the drive towards progress.
Furthermore, VR serves as a potent tool in fostering cultural preservation and global connectivity, allowing us to explore and appreciate the rich tapestry of human history and cultural heritage from a new vantage point. As we continue to innovate and expand the boundaries of what VR technology can achieve, it beckons a future where our interaction with the digital and physical worlds becomes more harmonized and enriching.
In conclusion, the road ahead for VR is replete with potential and opportunities. As we navigate this evolving landscape, it invites us to reimagine the contours of reality, fostering a world that is more inclusive, empathetic, and attuned to the nuances of human experience. The advantages of VR are not merely technological; they resonate on a profound level, ushering us into a new epoch of innovation and human connectivity.