Real Examples and Use Cases of Metaverse in Tourism
Posted on September 17, 2024 4 minutes 737 words
Table of contents
Introduction
The fusion of virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) technologies has given birth to the metaverse, a collective virtual shared space that is redefining interaction and engagement across various sectors—including tourism. This blog post delves deeply into how the metaverse is revolutionizing tourism, providing immersive experiences that transcend traditional travel limitations. We will explore detailed use cases and real-world examples where the metaverse has enhanced the travel experience, offering insights into this burgeoning field.
What is the Metaverse?
The metaverse can be conceptualized as a seamless blend of digital and physical realities, where enhanced virtual experiences and stable virtual spaces converge. It’s a realm where augmented reality, virtual worlds, and the vast expanse of the internet merge to create interactive environments that mimic and transcend real-world limitations.
Use Cases of Metaverse in Tourism
1. Virtual Destination Tours
Overview:
Virtual destination tours are a cornerstone of metaverse applications in tourism. These tours replicate real-world environments in a virtual context, allowing users to navigate and explore distant locales without leaving their homes. The technology not only caters to convenience but also enhances accessibility, offering a glimpse of mobility without physical boundaries.
Real Example:
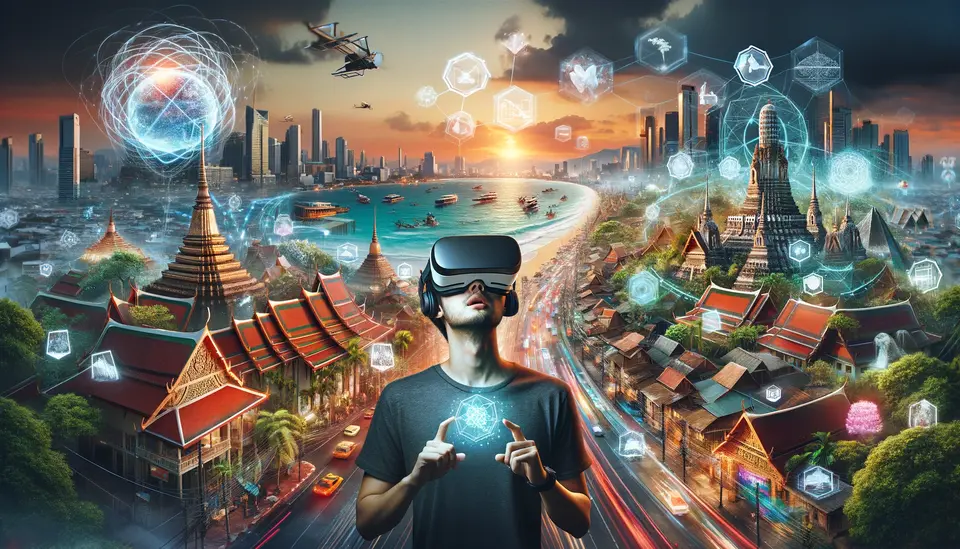
The Thailand Virtual Tour: Launched by the Tourism Authority of Thailand, this initiative offers a comprehensive virtual experience of Thailand’s top sights. From the bustling streets of Bangkok to the serene beaches of Phuket, users can enjoy a fully immersive exploration through a VR headset. The project aims to boost tourism interest and global engagement without the carbon footprint of actual travel.

2. Planning and Booking Experiences
Overview:
Planning trips can be daunting due to the uncertainty about facilities and experiences. The metaverse offers potential travelers tools to virtually visit hotels, restaurants, and major attractions to make informed decisions about their itineraries and accommodations.
Real Example:
Amadeus Navigation Solutions: Amadeus, a leading travel technology company, has developed virtual reality solutions that allow users to virtually “walk” into a hotel room or “sit” in a plane seat during the booking process. This immersive preview significantly enhances customer satisfaction and helps reduce booking hesitations.
3. Enhanced On-site Experiences
Overview:
Augmented reality significantly enriches tourist experiences at actual destinations by overlaying helpful information and interactive features onto the physical world. This can range from historical data and navigation aids to real-time translation services, all displayed through AR devices.
Real Example:
AR Historical Sites Tours: Companies like ARtGlass deploy AR technology at cultural heritage sites across Europe. By wearing AR glasses, visitors can see historical reenactments, architectural reconstructions, and multilingual narrations superimposed on the ruins, thereby deepening the educational value of their visit.
4. Accessibility
Overview:
The metaverse can tailor travel experiences to meet the unique needs of individuals with disabilities, offering virtual previews of locales, accommodations, and transport options to ensure they are accessible and safe.
Real Example:
Virtual Barrier-Free Tours: These virtual tours are designed to be inclusive, allowing individuals with mobility challenges, as well as those who are visually or hearing-impaired, to experience global destinations. These tours often include customized VR content that is accessible and engaging, opening up a world of travel opportunities to those who might face physical travel barriers.
5. Training and Education
Overview:
VR in the metaverse also serves as an effective training platform for tourism professionals. It enables realistic simulations of various scenarios—both routine and challenging—thus preparing staff better for real-world interactions and enhancing service quality.
Real Example:
Marriott Hotel’s VR Training: Marriott International utilizes VR to simulate diverse customer service scenarios for training its staff. From handling check-ins to managing complex guest requests, employees experience immersive simulations that improve their problem-solving skills and readiness for actual customer interactions.
Future Trends
Increased Personalization: As AI technology evolves, personalized travel experiences could be created based on individual preferences collected through data, offering tailor-made itineraries and activities in the metaverse.
Sustainable Tourism: Virtual tourism could significantly reduce the need for physical travel, which in turn would minimize the environmental degradation associated with traditional tourism.
Integration with Other Technologies: Ongoing advancements in AI, IoT, and blockchain could integrate more deeply with the metaverse to streamline and secure travel experiences, making them more seamless and immersive than ever before.
Conclusion
The integration of the metaverse into the tourism industry promises to make travel more inclusive, sustainable, and thrilling. The aforementioned examples illuminate the pathway towards a future where our travel experiences are no longer bounded by physical constraints but are enriched by virtual innovations.