History of Metaverse: In-Depth Look
Posted on July 26, 2023 19 minutes 3981 words
Table of contents
I. Introduction
A. The Metaverse: A Digital Universe Unfolds
The term ‘metaverse’ may sound like it was extracted directly from a science fiction novel - and for good reason. The term originates from Neal Stephenson’s 1992 cyberpunk classic, ‘Snow Crash,’ where it describes a virtual reality-based successor to the internet. In Stephenson’s vision, the metaverse is a collective virtual shared space, created by the convergence of physically virtually enhanced reality and the internet’s vast network.
In a practical sense, today’s metaverse refers to a digital universe filled with multiple interconnected virtual worlds. Each world can be incredibly diverse, ranging from fully immersive virtual realities to augmented realities that blend the physical and digital. It’s a space where users can interact with a computer-generated environment and other users in real time.
B. The Metaverse: The Digital Frontier
The importance and relevance of the metaverse in today’s digital world can hardly be overstated. The internet has opened up new avenues for interaction, commerce, and entertainment. The metaverse is viewed as the next significant evolution of this digital connectivity – a place where these interactions are not just facilitated, but take on a whole new dimension of immersion and continuity.
The metaverse is envisioned as a persistent digital universe that exists 24/7, accessible from a variety of devices, and inhabited by millions of users and autonomous digital entities. The potential applications are incredibly diverse, from virtual social spaces and gaming to new forms of online commerce (meta-commerce) and digital art spaces. Its impact could be as significant as the internet itself, reshaping how we work, socialize, learn, and entertain ourselves.
C. Glimpses of the Metaverse: A Historical Preview
In this blog post, we embark on an exciting journey tracing the metaverse’s evolution. From early virtual reality concepts and the internet’s development, to the breakthroughs in technology enabling the metaverse, we’ll explore how this fascinating concept has grown into a tangible reality.
We will delve into early influences and the key drivers that molded the concept of the metaverse. We’ll traverse the landscape of the metaverse’s modern incarnations, highlighting case studies from major players and exploring the ethical and regulatory challenges that the metaverse presents. Finally, we’ll peek into the crystal ball to imagine the future of the metaverse.
Join us on this journey, as we uncover the genesis, growth, and future trajectory of the metaverse, the digital frontier that promises to redefine the boundaries of interaction, creativity, and shared experiences.
II. Early Concepts and Influences
A. The Dawn of Virtual Reality (1960s-1980s)
The roots of the metaverse concept can be traced back to the early days of virtual reality (VR). The 1960s witnessed the birth of the first VR systems, though they were far from the consumer-friendly devices we know today. In 1962, Morton Heilig patented the Sensorama, a machine he described as the “Cinema of the Future.” It was designed to stimulate all five senses, attempting to fully immerse the user in a virtual world.
The term ‘virtual reality’ itself was popularized in the 1980s by Jaron Lanier, the founder of the visual programming lab (VPL). VPL Research developed several pioneering VR devices, including the Dataglove and the EyePhone Head-Mounted Display. Although these early systems were primitive and unwieldy by today’s standards, they laid the essential groundwork for the immersive virtual worlds that would become a core part of the metaverse.
B. Literary Foundations: “Snow Crash” and “The Metamorphosis of Prime Intellect”
Neal Stephenson’s “Snow Crash” (1992) was instrumental in popularizing the term ‘metaverse’ and imagining what it might look like. In the novel, the metaverse is a virtual reality-based successor to the internet, a collective virtual shared space that users can access and interact within. Characters in the book use avatars to exist within the metaverse and interact with its digital inhabitants. This book brought the idea of a fully immersive, richly detailed, and interactive virtual world to the fore of public imagination.
Another significant literary work is Roger Williams’ “The Metamorphosis of Prime Intellect” (1994). The novel explores a world where a super-intelligent AI has reshaped reality into a form of metaverse, where humans can engage in experiences limited only by the laws of physics. The profound ideas and questions raised by this novel continue to influence discussions about the nature, potential, and pitfalls of a fully-realized metaverse.
C. The Early Forerunners: Multi-User Dungeons (MUDs) and Massively Multiplayer Online Role-Playing Games (MMORPGs)
In the early days of the internet, text-based multiplayer real-time virtual worlds known as Multi-User Dungeons, or MUDs, were among the first practical implementations of shared virtual spaces. Although they lacked the graphical interfaces of modern metaverses, MUDs pioneered many of the interactive and social features now common in virtual worlds.
The advent of graphical user interfaces and increasingly powerful computer hardware led to the creation of Massively Multiplayer Online Role-Playing Games (MMORPGs). Games such as ‘Ultima Online’ and ‘World of Warcraft’ offered shared, persistent worlds where thousands of players could interact, socialize, and embark on adventures. These games pushed the boundaries of shared virtual experiences and were crucial stepping stones towards today’s metaverse.
This early era of exploration, both in technology and literature, seeded the concepts that would eventually evolve into the modern understanding of the metaverse. From the inception of virtual reality to the shared worlds of MUDs and MMORPGs, the foundations were laid for an interconnected digital universe that is the metaverse of today.
III. Development and Maturation of the Internet
A. The Internet: The Metaverse’s Essential Foundation
The internet has been pivotal in shaping the metaverse concept. As a globally interconnected network, the internet enabled people from all over the world to connect, share information, and collaborate in unprecedented ways. The internet’s framework provided the backbone for developing shared, virtual spaces, laying the groundwork for the concept of the metaverse.
Furthermore, the internet’s evolution played a crucial role in molding the metaverse. In its early years, the internet was largely a static medium – a vast repository of linked documents where interactivity was limited. As technology evolved, so did the internet, morphing into a platform where users could interact not only with the content but with each other, creating a more dynamic and social experience. This social, interactive layer of the internet set the stage for the development of the metaverse’s shared, interactive virtual spaces.
B. The Rise of Web 2.0: User-Generated Content, Interactivity, and Social Networking
The advent of Web 2.0 marked a significant shift in how users interacted with the internet. No longer just consumers of information, users became creators. Blogs, wikis, video sharing platforms, and social media networks empowered users to generate their own content and share it with the world.
This user-generated content brought a level of dynamism and personalization to the internet, traits essential for the metaverse. Moreover, the rise of social networking platforms such as Facebook, Twitter, and Instagram signaled the growing importance of social interactions in the digital world, a core aspect of the metaverse.
Web 2.0 also introduced new levels of interactivity to the internet. Users could comment, like, share, and directly participate in the digital experience. This interactive nature is at the heart of the metaverse, where user interactions define the environment and contribute to its continual evolution.
C. The Birth of Internet-Based Virtual Worlds: Second Life and World of Warcraft
With the maturation of the internet and the advent of Web 2.0, the stage was set for more complex, interactive virtual worlds to emerge. Two platforms, in particular, stood out during this period – Second Life and World of Warcraft.
Launched in 2003, Second Life was one of the first internet-based virtual worlds that allowed users to live a parallel life online. Unlike traditional games, Second Life did not have a set objective. Instead, it offered users a platform to explore, interact, and create in a user-generated world. Players could create avatars, buy virtual real estate, build structures, form relationships, and even start businesses.
World of Warcraft (WoW), launched in 2004, took a different approach, combining the features of MMORPGs with a vast, immersive world. WoW provided a shared, persistent environment where players could embark on quests, form alliances, and compete against each other. The social and interactive nature of WoW made it a precursor to the metaverse, demonstrating the potential for richly detailed, shared virtual spaces.
Both Second Life and World of Warcraft demonstrated the possibilities of virtual social interactions and shared experiences on the internet. These platforms were instrumental in shaping the idea of the metaverse as a space for social connection, creativity, and exploration.
IV. Technological Advances Enabling the Metaverse
A. The Trifecta: Faster Internet, Cloud Computing, and Advanced Graphics Hardware
The advent and evolution of the metaverse have been strongly influenced by technological advancements in various fields. Notably, faster internet speeds, the rise of cloud computing, and advanced graphics hardware have all played significant roles in shaping the metaverse.
High-speed internet has enabled the seamless, real-time interaction that is crucial for the metaverse. It has facilitated the delivery of high-quality, immersive experiences to users around the globe, making the metaverse more accessible and engaging.
Cloud computing, with its scalable and flexible resources, has also been instrumental. It has allowed for the processing power required to generate and maintain the complex, persistent virtual worlds of the metaverse. With cloud technology, even users with less powerful hardware can access and enjoy the metaverse’s rich, interactive experiences.
Moreover, advancements in graphics hardware have made the rendering of detailed, lifelike virtual environments possible. Technologies like ray-tracing, which models the way light interacts with virtual objects, and advances in GPU technology have contributed significantly to the visual fidelity of metaverse experiences.
B. The VR/AR Revolution: Bridging the Gap Between the Physical and Virtual
The proliferation of modern virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) technologies has been key to the metaverse’s evolution. These technologies offer immersive, interactive experiences that blur the line between the physical and digital worlds – a central concept of the metaverse.
VR technologies, such as Oculus Rift, HTC Vive, and PlayStation VR, provide fully immersive experiences that transport users into virtual environments. They’re instrumental in realizing the metaverse’s potential as a platform for immersive entertainment, social interaction, and virtual tourism.
On the other hand, AR technologies overlay digital information onto the physical world, enhancing real-world interactions with digital content. This is evident in applications like Pokémon Go and AR filters on social media platforms. In the context of the metaverse, AR can serve to integrate digital and physical realities, extending the metaverse into everyday life.
C. The Blockchain Boom: Cryptocurrencies and Beyond
Blockchain technology and cryptocurrencies have also had a profound impact on the metaverse’s development. The decentralized nature of blockchain offers a model for a metaverse that isn’t controlled by any single entity. This aligns with visions of an open metaverse that respects user sovereignty and promotes decentralized development.
Cryptocurrencies, including Bitcoin and Ethereum, along with the concept of smart contracts, provide mechanisms for secure, transparent transactions within the metaverse. They enable digital ownership and commerce, contributing to the creation of fully functioning virtual economies.
More recently, Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs) have introduced a way to create, buy, and sell unique digital assets in the metaverse. This has massive implications for digital art, real estate, and other forms of ownership in the metaverse, fueling further growth and innovation in these virtual spaces.
These key technologies have not only made the concept of the metaverse feasible but also continue to shape its ongoing evolution. As they advance further, the potential and capabilities of the metaverse are likely to grow exponentially.
V. The Modern Metaverse: Case Studies
A. Case Study: Facebook (Meta) and the Vision for a Social Metaverse
In 2021, Facebook announced a corporate name change to Meta Platforms Inc., or Meta for short, highlighting its ambitious strategy to build a next-generation internet known as the metaverse. Meta’s vision of the metaverse is a persistent, shared, online 3D virtual space that links physical reality with digital experiences.
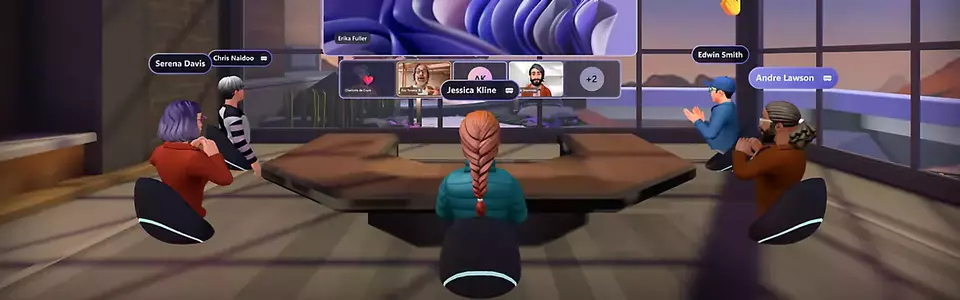
Meta’s approach to the metaverse revolves heavily around social interactions. The company is investing in technologies like advanced VR/AR, AI, and high-speed connectivity to create interactive, immersive spaces where people can play, work, learn, and connect with each other. A key element of this vision is embodied in the development of their VR platform, Horizon Workrooms, which provides a virtual environment for remote collaboration.
Meta’s push towards the metaverse has the potential to revolutionize not just social media but how we interact with the digital world as a whole. Their comprehensive approach, spanning from hardware like Oculus VR headsets to software platforms for social connection, indicates a future where digital and physical realities are increasingly intertwined.

B. Case Study: Decentraland and the Blockchain-Based Metaverse
Decentraland is a unique example of a blockchain-based metaverse. It is a decentralized virtual world where users can own and control digital real estate, represented as non-fungible tokens (NFTs) on the Ethereum blockchain. In Decentraland, users can build, buy, and sell virtual property and objects, effectively creating a self-governed, digital economy.
Unlike many other virtual worlds, Decentraland is not controlled by a single organization. Instead, it’s governed by a decentralized autonomous organization (DAO), where users vote on policies and changes to the platform. This democratic approach gives users a direct stake in the development and governance of the metaverse.
Decentraland exemplifies how blockchain technology can be used to create decentralized, user-driven metaverses. It provides valuable lessons on digital ownership, decentralized governance, and the creation of virtual economies.
C. Case Study: Fortnite and the Gaming Metaverse
Fortnite, developed by Epic Games, is often cited as a precursor to the gaming metaverse. Although it started as a battle royale game, Fortnite has evolved into a platform for shared experiences that go beyond traditional gaming.
Epic Games has transformed Fortnite into a social space where players can hang out, explore, and participate in non-gaming activities. The game has hosted virtual concerts, film screenings, and interactive narratives, blurring the lines between gaming, entertainment, and social networking.
Fortnite represents a gaming-centric approach to the metaverse, demonstrating how video games can serve as platforms for a wide array of shared, interactive experiences. Its success highlights the potential of the metaverse as an all-encompassing digital entertainment platform.
D. Case Study: Microsoft and the Enterprise Metaverse
Microsoft’s vision for the metaverse focuses on the enterprise sector, leveraging mixed reality and AI technologies to enhance collaboration and productivity. Their approach is embodied in Mesh, a platform that allows people in different locations to join shared virtual experiences on a variety of devices.
Microsoft’s Mesh can create immersive meetings where participants, represented by avatars or holoportation, can interact with 3D content and each other. This allows for a level of interaction and collaboration that is hard to achieve with traditional video conferencing.
With its enterprise-focused approach, Microsoft demonstrates the potential for the metaverse to transform not just how we socialize and entertain ourselves, but also how we work. It showcases the potential of the metaverse in driving the future of remote work, collaboration, and professional training.
Each of these case studies represents different facets of the metaverse’s potential and provides valuable insights into how different sectors—social media, blockchain, gaming, and enterprise—can harness the metaverse’s capabilities. They reflect the diversity of the metaverse and highlight the myriad ways it can revolutionize digital experiences.
VI. Regulation and Ethical Considerations
A. Privacy and Security in the Metaverse
As the metaverse expands, issues concerning privacy and security become increasingly complex and critical. In a realm where personal and professional interactions take place in a shared, persistent digital environment, protecting personal data, and maintaining confidentiality becomes crucial.
Given the breadth and depth of user interactions within the metaverse, a massive amount of personal data can be generated, from basic user information to behavioral data and even biometrics in VR/AR-based metaverses. This raises significant questions: How is this data stored and used? Who has access to it? What is the potential for misuse?
In addition to privacy concerns, security issues are paramount. The metaverse, like any digital environment, can be susceptible to hacking, digital theft, and other cybercrimes. Ensuring robust security protocols and safeguards is vital to protect user data, digital assets, and to maintain trust in the metaverse.
B. Legal and Regulatory Challenges
The metaverse presents a plethora of unique legal and regulatory challenges. Traditional legal frameworks may not be well suited to addressing the complexities of a decentralized, global, digital environment that blurs the boundaries between the physical and virtual worlds.
Issues around digital property rights, for instance, are a significant area of concern. In a world where digital assets can have real-world value, clearly defining ownership and property rights is critical. The application of blockchain and NFTs, which can ensure unique ownership of digital assets, provides a solution but also introduces new legal complexities.
Moreover, jurisdictional issues can arise in a globally accessible metaverse. In case of disputes or illegal activities, which country’s laws apply? How can regulations be enforced in a decentralized, borderless environment?
Addressing these challenges requires innovative legal thinking and potentially new laws and regulations tailored for the metaverse. It’s likely that a collaborative approach, involving lawmakers, technologists, and the users of the metaverse, will be necessary to create effective regulatory frameworks.
C. Ethical Considerations
The metaverse also prompts a host of ethical considerations. These spaces often encourage user freedom and self-expression, but how should these be balanced against potential harms? Issues of harassment and harmful behavior in virtual environments are real and can have significant impacts on individuals and communities.
Moreover, given the immersive nature of the metaverse, content moderation becomes a particularly sensitive issue. Determining what constitutes acceptable behavior and content in the metaverse can be challenging, especially given its global nature and cultural diversity.
The question of accessibility and equity also arises. As the metaverse becomes an increasingly important space for work, socialization, and leisure, it’s crucial to ensure that it is inclusive and accessible to all, regardless of socioeconomic status, physical ability, or geographical location.
The metaverse, with its immense potential and novelty, inevitably prompts significant privacy, legal, and ethical considerations. Navigating these will be crucial to its development, requiring a nuanced understanding of the metaverse’s unique attributes, ongoing dialogue among stakeholders, and potentially new regulatory and ethical frameworks.
VII. Future of the Metaverse
A. Emerging Trends and Developments
The metaverse continues to evolve at a rapid pace, shaped by several key trends and developments. The integration of AI, for instance, is poised to enhance the dynamism and interactivity of virtual worlds. Advanced AI can create more lifelike non-player characters, realistic environmental changes, and personalized experiences based on user behavior and preferences.
Moreover, we’re witnessing an increasing convergence of the metaverse with physical reality, fueled by advancements in AR and Internet of Things (IoT) technologies. This trend towards an “AR Cloud” or “Mirror World” points towards a metaverse that isn’t purely virtual but closely tied to our physical environment, overlaying digital information onto the real world.
The application of blockchain and cryptocurrencies is another major trend shaping the metaverse. Beyond facilitating digital ownership and commerce, these technologies offer a model for a decentralized metaverse, where power and control are distributed among users, not concentrated in single entities.
B. Potential Future Applications and Implications
As these trends unfold, a myriad of new applications and implications of the metaverse are anticipated. In terms of social interaction and entertainment, we can expect ever more immersive and diverse experiences, from virtual concerts and sporting events to new forms of social media and interactive storytelling.
The metaverse also holds significant potential for work and education. Virtual offices and classrooms could become commonplace, offering novel ways to collaborate, learn, and innovate. With its ability to simulate real-world situations, the metaverse could also revolutionize training and skill development in various fields.
Furthermore, the metaverse could drive significant economic activity. The growth of virtual economies, where real value is generated through the creation, exchange, and consumption of digital goods and services, could transform economic landscapes. The implications for industries like real estate, retail, and entertainment are profound.
C. The Metaverse in the Next Decade
Projecting the shape of the metaverse in the next decade is an inherently speculative endeavor, given the pace of technological change and the novelty of the concept. However, based on current trends, we can make some informed conjectures.
The metaverse of the future is likely to be a seamless blend of physical and digital realities, rather than a purely virtual space. Advanced AR technologies, IoT, and ubiquitous, high-speed connectivity will weave digital experiences into our everyday physical world.
The metaverse is also likely to be more decentralized than current digital platforms. Blockchain technologies could provide the infrastructure for a user-governed metaverse, where users have true ownership over their digital assets and a say in the development and governance of the space.
Furthermore, the boundary between ‘user’ and ‘creator’ will blur in the metaverse. With accessible creation tools and user-generated content, everyone will have the ability to shape their environment and experiences, leading to a highly diverse and dynamic metaverse.
In conclusion, the future of the metaverse is incredibly exciting. While challenges and uncertainties lie ahead, the potential of the metaverse to revolutionize how we interact, work, learn, and play is immense. As we continue to navigate and shape this brave new digital world, the only certainty is that the metaverse will continue to surprise and innovate.
VIII. Conclusion
A. Recap of the Evolution of the Metaverse
The metaverse, as we’ve seen, is not an entirely new concept, but rather the culmination of decades of progress in various fields, from computing and internet technology to virtual reality, gaming, and blockchain. The journey of the metaverse began with early experiments in shared virtual spaces in the 1960s and 70s, took inspiration from science fiction in the 80s and 90s, and matured with the growth of the internet and virtual worlds in the late 90s and 2000s.
In recent years, we’ve seen the acceleration of this evolution, spurred by advances in hardware and software technologies, internet connectivity, and the growth of blockchain. The metaverse has evolved from a theoretical concept to an increasingly tangible reality, with platforms like Meta’s Horizon, Decentraland, Fortnite, and Microsoft’s Mesh paving the way.
B. The Metaverse: A Future Unfolding
Today, the metaverse stands at the intersection of technology and society, its potential only just beginning to be realized. Its importance lies not just in its technological innovation but in its potential to reshape our interactions, economies, and societies.
The metaverse offers an opportunity for us to redefine how we connect, work, and learn. It has the potential to become an all-encompassing platform for human experience, blurring the lines between the physical and digital worlds, and between gaming, socializing, and professional activity.
However, as with all transformative technologies, it also brings challenges and dilemmas. Issues of privacy, security, regulation, and ethics are paramount. Navigating these challenges requires foresight, inclusive dialogue, and regulatory innovation.
Looking ahead, the metaverse will continue to evolve and surprise us. As technologies advance, new uses emerge, and societies adapt, the metaverse of the future may look very different from what we imagine today. It’s an exciting journey we are embarking on, full of possibilities, challenges, and unknowns. As we traverse into this new era, we are not just passive observers but active participants, shaping and being shaped by the metaverse.
In conclusion, the metaverse represents a significant evolution in how we interact with digital technologies. As we continue to explore this new frontier, it promises to transform our digital experiences and potentially, our societies in profound ways. It’s a journey that we are just beginning, and one that will undoubtedly continue to evolve and surprise us in the years to come.