15 Examples of the Use of Augmented Reality (AR) in Training
Posted on April 27, 2023 5 minutes 877 words
Table of contents
- 1. Medical Training and Simulation
- 2. Emergency Response Training
- 3. Aviation and Aerospace Training
- 4. Military and Defense Training
- 5. Automotive Industry Training
- 6. Sports and Fitness Training
- 7. Retail and Sales Training
- 8. Construction and Architecture Training
- 9. Art and Design Training
- 10. Language Learning and Cultural Training
- 11. Manufacturing and Production Training
- 12. Logistics and Warehousing Training
- 13. Education and Classroom Training
- 14. Cybersecurity Training
- 15. Environmental and Conservation Training
- Conclusion
Augmented Reality (AR) has come a long way since its inception, and its impact on various industries is ever-growing. By merging the digital world with the physical, AR provides users with interactive, immersive, and engaging experiences. In this blog post, we’ll take a deep dive into 15 examples of how AR is transforming the landscape of training and education, and explore some real-world applications that showcase its potential.
1. Medical Training and Simulation
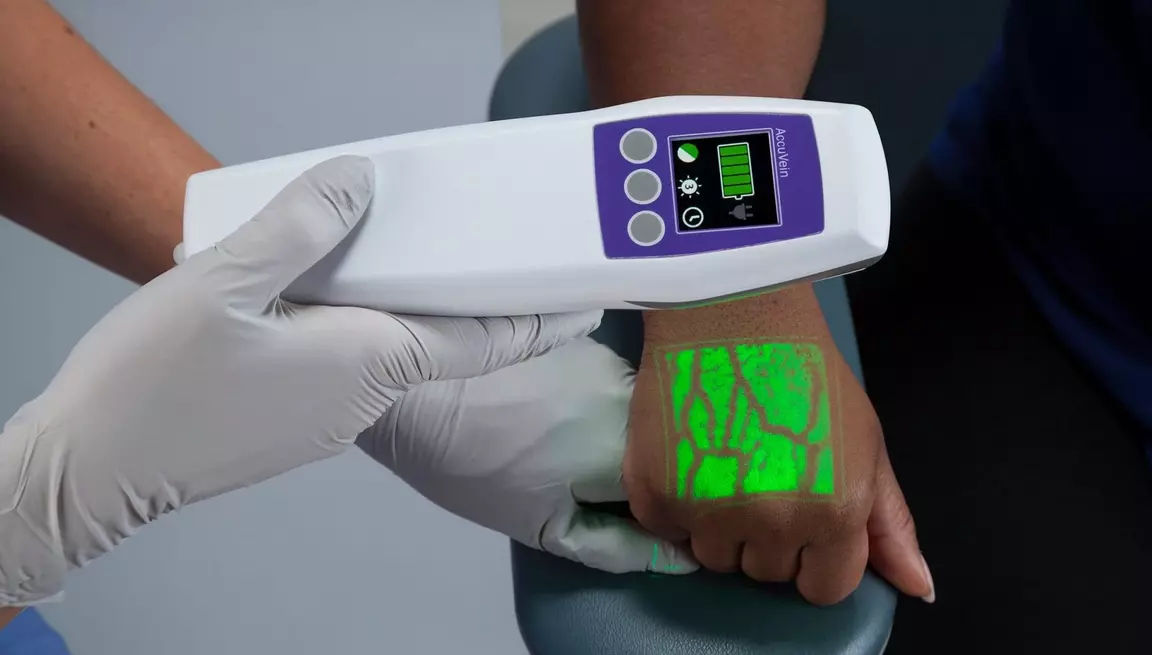
AR has revolutionized medical education by allowing students to practice surgeries, visualize internal organs, and comprehend complex procedures without risk to patients. One example is the AccuVein system, which uses AR to project veins onto a patient’s skin in real-time, enabling healthcare professionals to find veins more quickly and accurately.
2. Emergency Response Training
First responders and emergency management teams now use AR to prepare for crisis situations, search and rescue missions, and disaster management. For instance, the FLAIM Trainer system provides firefighters with realistic training scenarios using a combination of AR, VR, and haptic feedback to mimic the heat and weight of actual firefighting equipment.
3. Aviation and Aerospace Training
AR-based flight simulators provide realistic cockpit experiences, making aviation training more engaging and effective. An example is Aero Glass, an AR system for pilots that offers real-time flight data, such as altitude, airspeed, and flight path, on a heads-up display (HUD).
4. Military and Defense Training
The military has adopted AR to enhance combat training, vehicle maintenance, and mission planning. The Integrated Visual Augmentation System (IVAS) developed by Microsoft for the US Army combines AR, AI, and IoT technologies to provide soldiers with critical information, navigation assistance, and real-time analytics during field operations.
5. Automotive Industry Training
AR has transformed automotive training by helping technicians perform complex repairs, diagnostics, and assembly processes. For example, Porsche uses the Tech Live Look system, which connects technicians with remote experts using AR glasses, enabling real-time collaboration and faster problem-solving.
6. Sports and Fitness Training
AR improves athletic performance by providing virtual coaching, biomechanics analysis, and real-time feedback. The Ghost Pacer, an AR-based running app, allows users to race against a holographic avatar that follows a predetermined pace, helping them improve their speed and endurance.
7. Retail and Sales Training
AR enhances product demonstrations, sales pitches, and customer service scenarios. Lowe’s, a home improvement retail company, introduced the Holoroom, an AR-enabled space where customers can visualize home renovation projects and interact with virtual products before making a purchase.
8. Construction and Architecture Training
AR has streamlined site inspections, safety training, and building design visualization. The DAQRI Smart Helmet, for example, provides construction workers with real-time data about their surroundings, making it easier to identify hazards, collaborate on designs, and troubleshoot problems.
9. Art and Design Training
AR technology improves skills in painting, sculpture, and interior design by providing virtual environments for practice. Gravity Sketch, an AR design tool, allows artists and designers to create 3D sketches and models in mid-air, facilitating collaboration and experimentation.
10. Language Learning and Cultural Training
AR can enhance language learning through interactive conversations and immersive cultural experiences. Mondly, an AR language learning app, uses speech recognition and conversation simulations to help users practice speaking with virtual characters.
11. Manufacturing and Production Training
AR improves assembly line training, equipment maintenance, and quality control processes in the manufacturing sector. Boeing, for example, uses AR to guide technicians through complex wiring tasks in aircraft assembly, reducing errors and production time. Additionally, AR systems can be used to provide real-time information about equipment status, helping to minimize downtime and increase overall efficiency.
12. Logistics and Warehousing Training
AR technology trains workers in inventory management, loading and unloading processes, and safety procedures. DHL, a global logistics company, has piloted an AR program called “Vision Picking” that provides warehouse workers with real-time data on item locations, streamlining the picking process and reducing errors.
13. Education and Classroom Training
AR is transforming classrooms through interactive learning, STEM education, and virtual field trips. Google Expeditions, an AR app for educators, enables students to explore various locations, historical events, and scientific concepts in an immersive and engaging manner.
14. Cybersecurity Training
AR plays a crucial role in training professionals to identify and respond to cybersecurity threats through realistic simulations. Companies like Cyberbit offer AR-powered training solutions that simulate cyber-attacks on virtual networks, enabling trainees to practice their skills and develop effective defense strategies in a safe environment.
15. Environmental and Conservation Training
AR technology is increasingly being used for training individuals in ecological monitoring, wildlife conservation, and environmental restoration efforts. The U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service, for instance, has developed an AR app called “Nature Explorer” that helps users identify and learn about local wildlife, fostering a deeper understanding of natural ecosystems and the importance of conservation efforts.
Conclusion
The potential of augmented reality to revolutionize training in various fields is becoming more evident every day. By enhancing the quality and effectiveness of training programs, AR technology not only prepares professionals for their roles but also helps industries overcome challenges and drive innovation. As AR continues to evolve, we can expect to see even more transformative applications across different sectors, making training more engaging, efficient, and accessible for everyone.