What are the components of Smart Glasses?
Posted on April 23, 2023 4 minutes 809 words
Table of contents
Smart glasses have become increasingly popular in the tech market, offering a wide range of applications from fitness tracking to augmented reality experiences. In this blog post, we’ll take an in-depth look at the various components that make up smart glasses and discuss the future of this innovative technology.
Overview of Smart Glasses
Smart glasses are wearable devices that integrate digital displays and connectivity features into a comfortable and stylish form factor. They have evolved significantly since the early days of Google Glass, with notable brands like Apple and Microsoft entering the market with cutting-edge products such as Apple Glass and Microsoft HoloLens.
Display Technologies
There are several different display technologies used in smart glasses, each with its own unique benefits and limitations:
- Projection-based displays: Images are projected onto the glasses’ lenses, creating a virtual display. This type of display is easier to see in bright conditions, but may consume more power and offer a smaller field of view.
- Waveguide displays: Light is guided through a thin, transparent material and directed into the user’s eyes. This technology allows for a larger field of view and less power consumption, but may have lower brightness levels and require more precise alignment for optimal image quality.
- Direct retinal projection: Images are projected directly onto the wearer’s retina, providing a high-resolution image with minimal power consumption. However, this technology is still in development and not yet widely available in consumer products.
Sensors and Cameras
Smart glasses are equipped with a variety of sensors and cameras, such as:
- Accelerometers: Measure linear acceleration, allowing the glasses to track movement and orientation.
- Gyroscopes: Measure angular velocity, helping to stabilize the displayed image and track head movement.
- Ambient light sensors: Detect environmental light levels and adjust display brightness accordingly.
- Depth sensors: Enable 3D mapping and spatial awareness for augmented reality applications.
These components work together to enable features like gesture recognition, head tracking, and spatial awareness, allowing for a more immersive and interactive experience.
Audio Output and Microphone
Audio output in smart glasses is achieved through built-in speakers or bone-conduction technology, which transmits sound through the skull directly to the inner ear. This allows users to hear audio without obstructing their ears, maintaining situational awareness.
Microphones integrated into smart glasses enable voice commands and communication, allowing users to interact with the device hands-free.
Connectivity and Processors
Connectivity options like Bluetooth, Wi-Fi, and GPS are crucial for syncing data with smartphones or other devices and enabling location-based services. Processors used in smart glasses, such as ARM-based or custom-designed chips, ensure smooth performance and efficient power consumption.
Battery and Power Management
Battery technologies employed in smart glasses are typically lithium-polymer or lithium-ion batteries. Due to the compact size constraints of smart glasses, battery capacity is limited, which affects the overall design.
Power management strategies balance battery life and functionality, optimizing the user experience. Techniques such as dynamic power scaling, low-power display modes, and selective disabling of features can help extend battery life.
Software and Applications
Software platforms and operating systems used in smart glasses include Android, proprietary systems, or even modified versions of popular operating systems like iOS. These platforms support a wide range of applications designed specifically for smart glasses, offering diverse use cases, such as:
- Gaming: Augmented reality games that overlay digital content onto the real world.
- Productivity: Hands-free access to emails, calendars, and notifications.
- Navigation: Real-time directions and location-based information.
- Entertainment: Streaming video content and augmented reality experiences.
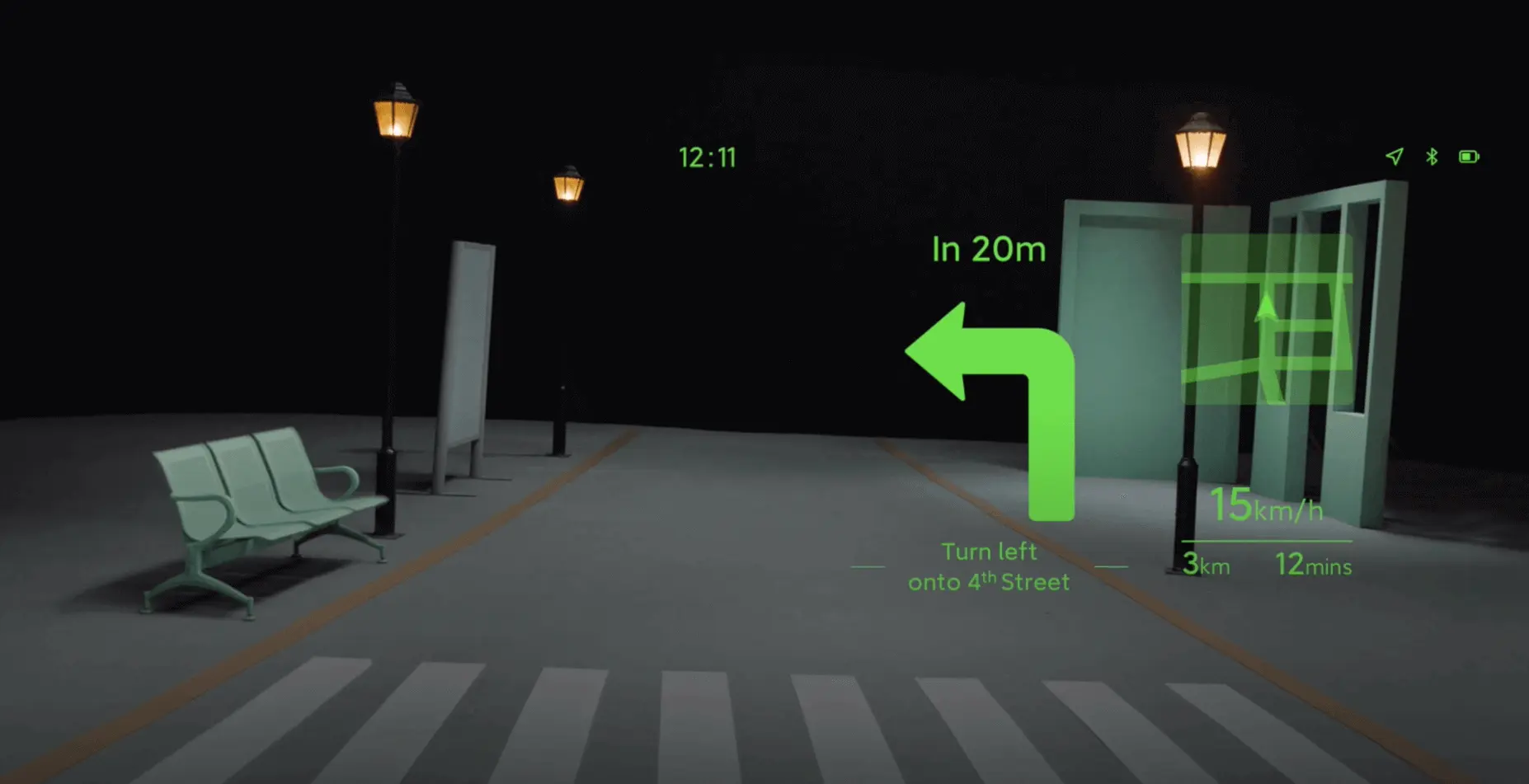

User Interface and Control Methods
Interacting with smart glasses can be accomplished through a variety of control methods, each with its own unique benefits and challenges:
- Touch controls: Some smart glasses feature touch-sensitive surfaces or buttons, allowing users to navigate menus and control functions with taps or swipes.
- Voice commands: Integrated microphones enable users to interact with smart glasses hands-free, issuing commands and dictating text input through voice recognition.
- Gesture recognition: Advanced sensors and cameras in smart glasses can detect specific hand gestures, enabling users to control the device without touching it.
Designing intuitive user interfaces for smart glasses is a significant challenge. Developers must balance simplicity with functionality while accommodating the limited screen real estate and varying interaction methods. Many smart glasses utilize a combination of these control methods, offering users multiple options for interacting with their devices.
Conclusion
In summary, smart glasses consist of a range of components, including display technologies, sensors, audio output, connectivity options, and more, which together are revolutionizing the way we interact with technology. As advancements in display technologies, battery life, and new applications continue to emerge, the future of smart glasses promises to be even more exciting and transformative. By understanding the components that make up these devices, we can better appreciate the potential impact of smart glasses on our daily lives and anticipate the innovations that lie ahead.