Virtual Reality (VR) for Pre-Treatment Visualization
Posted on January 25, 2024 7 minutes 1426 words
Table of contents
Introduction to Virtual Reality in Medicine
The realm of medicine has always been at the forefront of embracing revolutionary technologies, and the advent of Virtual Reality (VR) is no exception. Once a figment of science fiction, VR has rapidly evolved into a practical tool in various industries, most notably in healthcare. Its application in medicine extends beyond mere fascination, offering tangible benefits in patient care and medical training. In this realm, one of its most impactful uses is in pre-treatment visualization, a practice that is transforming the approach to surgical planning and patient engagement.
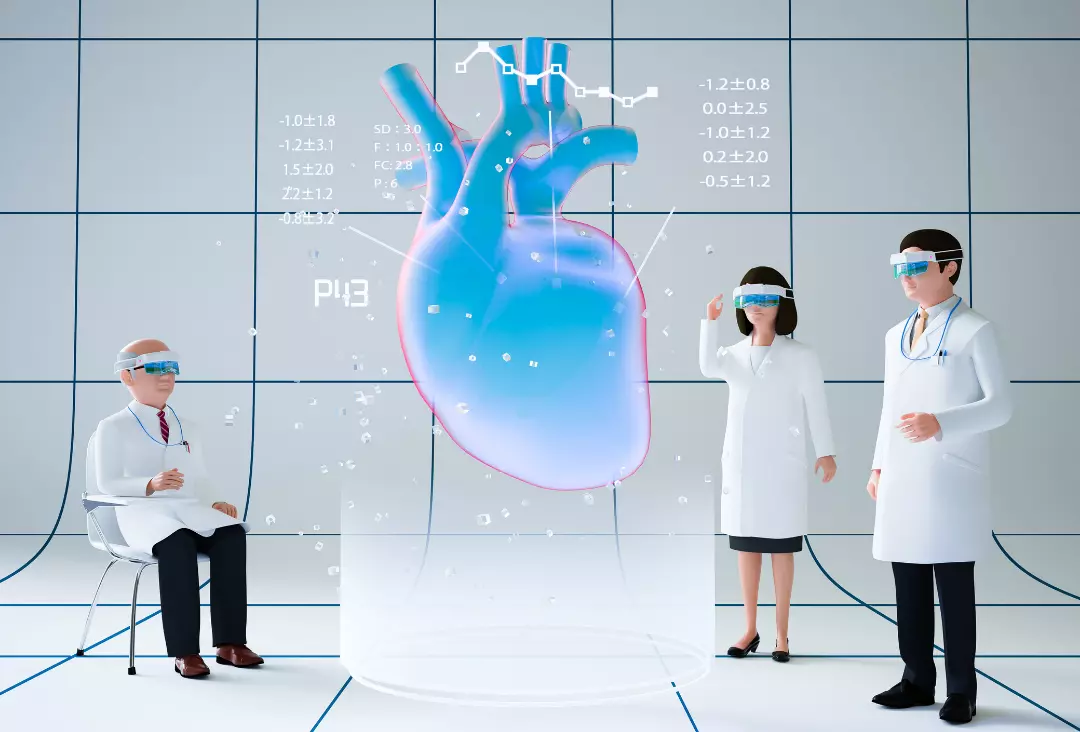
At its core, VR in medicine allows for an immersive, three-dimensional view of the human body. It transcends the limitations of traditional two-dimensional imaging techniques, like MRI or CT scans, offering a more comprehensive and intuitive understanding of complex anatomical structures. This capability is particularly crucial for medical professionals, especially those involved in surgical fields, as it provides a level of detail and spatial awareness previously unattainable.
Furthermore, VR’s role in pre-treatment visualization is not just a boon for professionals but also a bridge to better patient understanding and involvement. It demystifies complex medical procedures, making them more accessible and comprehensible to patients. This intersection of technology and medicine not only enhances the efficiency of healthcare delivery but also fosters a more collaborative doctor-patient relationship.
As we delve deeper into this blog post, we will explore the various benefits of VR in pre-treatment visualization, examine real-world applications and case studies, and speculate on future trends and developments. Virtual Reality in Medicine, particularly in pre-treatment visualization, is not just a technological advancement; it’s a paradigm shift in how we approach, understand, and execute medical care.
Benefits of VR for Pre-Treatment Visualization
Virtual Reality (VR) in medicine, particularly in pre-treatment visualization, has unlocked numerous benefits for healthcare professionals and patients alike. This section will explore the key advantages of integrating VR into medical practice.
Enhanced Understanding of Medical Conditions
- Three-Dimensional Insight: VR provides a unique three-dimensional perspective that is critical in understanding complex medical conditions. This depth of view allows surgeons to examine the intricacies of an affected area more thoroughly than traditional two-dimensional images.
- Interactive Experience: Unlike static images, VR offers an interactive experience. Surgeons can manipulate VR models, gaining a better understanding of the patient’s anatomy, leading to more accurate diagnoses and treatment plans.
Improved Surgical Planning and Patient Outcomes
- Precision in Surgical Planning: With VR, surgeons can plan surgeries with greater precision. This technology enables the rehearsal of surgical procedures, reducing the likelihood of unexpected challenges during actual surgeries.
- Reduced Risk of Complications: By practicing on a virtual model, surgeons can anticipate potential obstacles, which in turn reduces the risk of complications and improves patient outcomes.
Increased Patient Engagement and Education
- Enhancing Patient Understanding: VR can demystify complex surgical procedures for patients. By visualizing their own medical conditions through VR, patients gain a clearer understanding of their treatment, which can alleviate anxiety.
- Informed Decision Making: This increased understanding enables patients to make more informed decisions about their treatments, fostering a sense of control over their medical journey.
Incorporating these benefits into medical practice not only advances the field of surgery but also marks a significant step towards patient-centered care. The application of VR in pre-treatment visualization exemplifies how technology can enhance the efficiency and effectiveness of medical treatment.
Case Studies or Real-World Applications
Virtual Reality (VR) has not just been a theoretical advancement in medicine; it has concrete, real-world applications that have significantly impacted surgical planning and patient care. This section highlights a few key examples demonstrating the practical use of VR in medical settings.
Application in Complex Surgical Procedures
- Neurosurgery: In one notable case, VR was used to map out a complex brain surgery. The surgeon utilized VR to navigate through the patient’s brain structure, planning the safest and most effective route for tumor removal.
- Orthopedic Surgery: VR technology has also been instrumental in orthopedic surgery, allowing surgeons to virtually explore joint structures and plan procedures such as knee or hip replacements with enhanced precision.
Impact on Patient Care and Recovery
- Reduced Surgery Time: By pre-visualizing surgeries in VR, surgeons have reported reductions in operation time, which is beneficial for patient recovery and hospital resource management.
- Enhanced Rehabilitation: Post-surgery, VR has been used for patient rehabilitation, providing interactive and engaging exercises that can be tailored to the specific recovery needs of patients.
Integrating VR in Medical Training
- Educational Tool for Medical Students: VR serves as an excellent educational tool, providing medical students with immersive, hands-on experience without the risks associated with real-life surgeries.
- Continued Professional Development: For established medical professionals, VR offers opportunities for continued learning and skill enhancement, particularly in mastering new surgical techniques.
These case studies and applications underscore the transformative impact of VR in medicine, particularly in pre-treatment visualization. By offering practical, hands-on examples, this technology’s relevance and efficacy in improving surgical outcomes and patient care are vividly illustrated.
Future Trends and Potential Developments
The journey of Virtual Reality (VR) in medicine is just beginning. Its potential for growth and innovation is vast, promising to further revolutionize pre-treatment visualization and patient care. This section discusses upcoming trends and potential developments in this exciting field.
Advancements in VR Technology
- Higher Resolution and Realism: Future VR devices are expected to offer even higher resolution and more realistic simulations, enhancing the accuracy of pre-treatment planning and surgical rehearsals.
- Haptic Feedback Integration: The incorporation of haptic feedback, giving users a sense of touch, will significantly enhance the VR experience, allowing surgeons to feel textures and resistance as they would in real-life procedures.
Expanded Applications in Medicine
- Remote Surgical Assistance: With the advancement of VR, remote assistance in surgeries could become more prevalent, allowing expert surgeons to guide procedures from afar, breaking geographical barriers.
- Patient-Specific Models: The use of patient-specific VR models, generated from individual medical imaging, could become a standard practice, providing tailored surgical planning for each patient.
Addressing Challenges and Limitations
- Data Privacy and Security: As VR applications grow, addressing data privacy and security concerns will be crucial, especially when handling sensitive patient information.
- Accessibility and Cost: Efforts are needed to make VR technology more accessible and affordable for healthcare institutions globally, ensuring its benefits are not limited to high-resource settings.
Collaboration with Emerging Technologies
- Integration with AI and Machine Learning: Combining VR with AI and machine learning could lead to predictive models in pre-treatment planning, offering insights based on vast datasets of medical procedures and outcomes.
- Synergy with Other Technologies: The fusion of VR with other technologies like Augmented Reality (AR) and 3D printing could create comprehensive platforms for medical training and practice.
The future of VR in medicine holds exciting prospects, with the potential to further enhance patient care, surgical accuracy, and medical education. As these technologies evolve, they will undoubtedly unlock new possibilities in healthcare.
Conclusion: Implications for Patient Care and the Future of Medical Practice
As we have explored throughout this post, Virtual Reality (VR) in pre-treatment visualization is not just a technological novelty; it’s a significant advancement in the way medical professionals approach patient care. VR has the potential to revolutionize surgical planning, enhance patient understanding, and ultimately lead to better patient outcomes.
Enhancing the Standard of Care
The integration of VR in medical practice raises the standard of patient care. By providing detailed, three-dimensional views of medical conditions, VR enhances the ability of surgeons and medical staff to prepare for and execute complex procedures. This advancement not only benefits the medical professionals in terms of preparedness and confidence but also directly impacts patient safety and the success rates of surgeries.
Empowering Patients
One of the most remarkable aspects of VR in medicine is its role in patient empowerment. By visualizing their own medical conditions and the planned treatments in a VR environment, patients gain a much clearer understanding of their situation. This transparency is key to building trust and ensuring that patients are active participants in their own healthcare journey.
Looking Forward
The future of VR in medicine is bright and filled with possibilities. As technology continues to evolve, we can expect even more innovative applications, further enhancing the capabilities of medical professionals and improving the experiences of patients. The ongoing collaboration between technology developers and medical experts is crucial in driving these advancements forward.
In conclusion, Virtual Reality in medicine, particularly in pre-treatment visualization, represents a significant stride towards more precise, effective, and patient-centered healthcare. It’s a testament to how technology, when thoughtfully integrated, can enhance the very fabric of medical practice.