15 Examples of the Use of Virtual Reality (VR) in Military
Posted on April 9, 2023 8 minutes 1569 words
Table of contents
- 1. Combat Training Simulations
- 2. Vehicle and Aircraft Simulations
- 3. Medical Training
- 4. PTSD Treatment
- 5. Mission Planning and Rehearsal
- 6. Marksmanship and Shooting Training
- 7. Joint Operations Training
- 8. Explosive Ordnance Disposal (EOD) Training
- 9. Cultural Awareness and Language Training
- 10. Leadership Training
- 11. Counter-terrorism and Hostage Rescue Scenarios
- 12. Naval Training
- 13. Paratrooper Training
- 14. Cybersecurity Training
- 15. Maintenance and Repair Training
- Conclusion
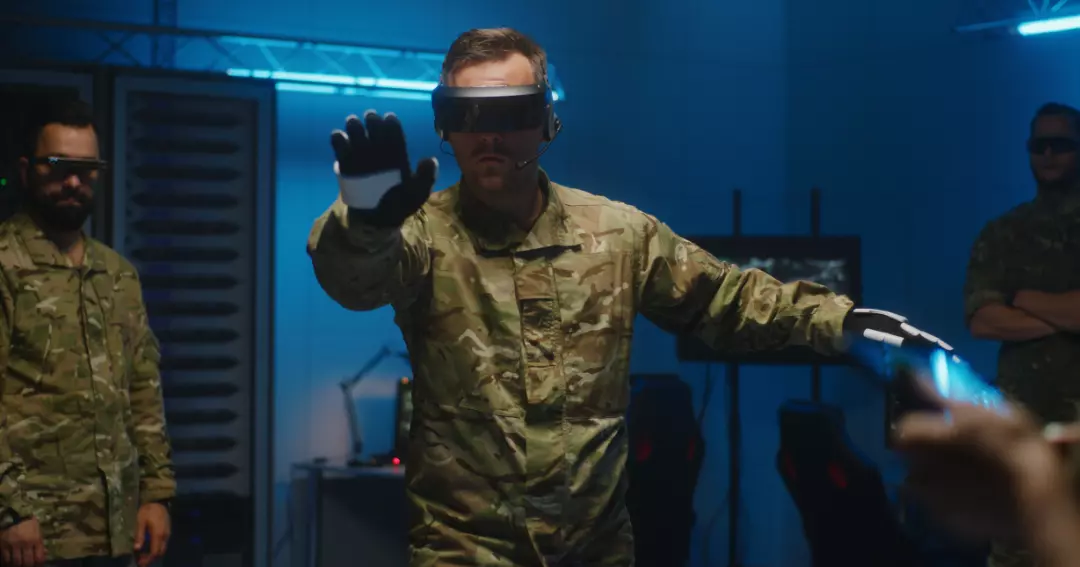
Virtual reality (VR) technology has transformed various industries, and the military is no exception. With its immersive, realistic environments, VR has become an essential tool in military training and operations. From combat simulations to language training, VR is being utilized in a wide range of applications by military forces around the world. In this blog post, we will explore 15 examples of how VR is being used in the military sector.
1. Combat Training Simulations
One of the primary applications of VR in the military is in combat training simulations. Soldiers can be immersed in realistic scenarios that replicate the challenges they may face in the field. By using VR, soldiers can improve their response time, situational awareness, and teamwork. VR simulations can be tailored to different types of terrain, weather conditions, and enemy tactics, allowing soldiers to practice various scenarios before facing them in real life.
For example, the United States Army has developed a VR combat simulator called Virtual Battlespace 3 (VBS3), which provides a realistic environment for training soldiers in a variety of situations. VBS3 can simulate urban combat, convoy operations, and even nuclear, biological, and chemical (NBC) warfare scenarios.
2. Vehicle and Aircraft Simulations
VR is also being used to train military personnel in the operation of vehicles and aircraft. Simulations can provide a cost-effective and safe way for pilots and vehicle operators to practice their skills without risking valuable equipment or human lives. By using VR, pilots and vehicle operators can be trained to handle different types of terrain, weather conditions, and enemy threats.
For instance, the United States Air Force uses VR to train pilots in various aircraft, including the F-35 Lightning II and the T-6 Texan II. These VR simulations allow pilots to practice flying in different conditions and scenarios, such as air-to-air combat, ground attack missions, and formation flying.
3. Medical Training
VR can also be used to train military medics in life-saving procedures in realistic scenarios. By simulating emergency situations, medics can improve their ability to perform under stress and make critical decisions. VR can also provide an opportunity for medics to practice procedures that they may not have encountered before, improving their overall skill set.
For example, the Israeli Defense Forces (IDF) uses VR to train their medics in treating battlefield injuries. The VR simulations provide a realistic environment for medics to practice triage, wound management, and other life-saving procedures.
4. PTSD Treatment
Virtual reality exposure therapy (VRET) is a treatment for post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) that involves gradually exposing patients to traumatic memories in a controlled environment. VRET can be used to treat veterans and other military personnel who have experienced traumatic events.
For instance, the Walter Reed Army Medical Center in the United States uses VR to treat veterans with PTSD. The VR simulations recreate the sights, sounds, and smells of the traumatic event, allowing the patient to confront their fears and learn coping strategies.
5. Mission Planning and Rehearsal
VR can also be used for mission planning and rehearsal. By creating a 3D environment of the mission area, commanders can visualize and plan missions, reducing the risks associated with planning on paper or maps. VR simulations can also provide an opportunity for soldiers to rehearse missions before deployment, improving their overall readiness.
For example, the United States Marine Corps uses VR to plan and rehearse missions. The VR simulations allow Marines to practice different scenarios and tactics, improving their overall effectiveness in the field.
6. Marksmanship and Shooting Training
VR-based shooting simulators provide a safe and controlled environment for soldiers to practice marksmanship and weapon handling. By using VR, soldiers can improve their accuracy and reaction time. The simulations can also provide a variety of scenarios that replicate different shooting situations, such as urban combat, long-range sniping, and close quarters battle.
For instance, the United States Army uses VR shooting simulators called Engagement Skills Trainer (EST) and Close Combat Tactical Trainer (CCTT). These simulators provide soldiers with a realistic environment to practice marksmanship, weapon handling, and squad-level tactics.
7. Joint Operations Training
By connecting VR systems across different military branches, joint operations training can take place, enhancing coordination and communication between forces. VR simulations can replicate the different equipment and tactics used by different branches of the military, allowing soldiers to practice working together in realistic scenarios.
For example, the United States Navy uses a VR simulation called the Littoral Combat Ship (LCS) Virtual Trainer, which provides joint operations training for sailors and Marines. The simulator replicates the different equipment and scenarios that the LCS may encounter, allowing sailors and Marines to practice working together in a realistic environment.
8. Explosive Ordnance Disposal (EOD) Training
EOD teams can practice defusing explosive devices in virtual reality, minimizing the risks associated with live training exercises. By using VR, EOD teams can practice different scenarios and techniques for defusing explosive devices, improving their overall readiness.
For example, the United States Army uses a VR simulation called the Virtual Interactive Explosive Ordnance Disposal System (VIEODS), which provides a realistic environment for EOD teams to practice their skills. The simulation can replicate different types of explosive devices and scenarios, such as a car bomb or a roadside bomb.
9. Cultural Awareness and Language Training
Virtual reality can create immersive environments that help soldiers learn about the culture and language of the regions where they’re deployed. By using VR, soldiers can improve their communication skills and understanding of local customs, improving relations with local populations.
For instance, the United States Army uses a VR simulation called the Tactical Language and Culture Training System (TLCTS), which provides soldiers with a realistic environment to practice communication and cultural awareness. The simulation can replicate different scenarios, such as a checkpoint or a village meeting.
10. Leadership Training
VR scenarios can help develop decision-making and leadership skills for officers, preparing them for complex situations they may face in the field. By using VR, officers can practice making critical decisions in a realistic environment, improving their overall leadership abilities.
For example, the United States Army uses a VR simulation called the Virtual Leader Trainer (VLT), which provides officers with a realistic environment to practice leadership and decision-making skills. The simulation can replicate different scenarios, such as a combat situation or a humanitarian mission.
11. Counter-terrorism and Hostage Rescue Scenarios
VR can be used to create realistic counter-terrorism and hostage rescue training scenarios. By simulating high-pressure situations, soldiers can improve their skills and response to these types of events.
For instance, the British Army uses a VR simulation called the Virtual Hostage Rescue Mission, which provides a realistic environment for soldiers to practice hostage rescue scenarios. The simulation can replicate different scenarios, such as a terrorist siege or a kidnapping situation.
12. Naval Training
VR can simulate various naval scenarios, from ship handling to damage control, providing a cost-effective and efficient way to train naval personnel. By using VR, sailors can practice different scenarios and tactics in a realistic environment, improving their overall effectiveness.
For instance, the Royal Navy of the United Kingdom uses a VR simulation called the Submarine Command System Trainer (SCST), which provides a realistic environment for submariners to practice command and control operations. The simulation can replicate different scenarios, such as a missile attack or a navigation emergency.
13. Paratrooper Training
Virtual reality can be used to simulate parachute jumps, allowing paratroopers to practice their skills without the need for costly and potentially dangerous live jumps. By using VR, paratroopers can practice different jump scenarios and techniques, improving their overall readiness.
For example, the United States Army uses a VR simulation called the Parachute Virtual Trainer (PVT), which provides a realistic environment for paratroopers to practice their skills. The simulation can replicate different jump scenarios, such as a high-altitude low-opening (HALO) jump or a static-line jump.
14. Cybersecurity Training
VR can create immersive simulations of cyber warfare scenarios, helping military personnel to better understand and respond to cyber threats. By using VR, soldiers can practice responding to different types of cyber attacks, improving their overall cybersecurity readiness.
For instance, the United States Air Force uses a VR simulation called the CyberPro VR, which provides a realistic environment for soldiers to practice responding to cyber attacks. The simulation can replicate different types of cyber threats, such as malware infections or denial-of-service attacks.
15. Maintenance and Repair Training
Using VR, soldiers can learn how to maintain and repair military equipment through interactive, step-by-step instructions in a realistic environment. By using VR, soldiers can practice different maintenance and repair scenarios, improving their overall technical readiness.
For example, the United States Army uses a VR simulation called the Maintenance Training Simulator (MTS), which provides soldiers with a realistic environment to practice maintaining and repairing military equipment. The simulation can replicate different equipment and scenarios, such as a tank engine repair or a helicopter rotor maintenance.
Conclusion
In conclusion, virtual reality has become an essential tool in military training and operations, with numerous applications that are revolutionizing the way military forces operate. From combat training simulations to cybersecurity training, VR provides a safe and cost-effective way for soldiers to practice different scenarios and techniques, improving their overall readiness and effectiveness. As technology continues to evolve, the applications of VR in the military sector are only set to expand, further enhancing the capabilities of military forces around the world.