15 Examples of the Use of Mixed Reality in Agriculture
Posted on May 9, 2023 5 minutes 870 words
Table of contents
- 1. Precision Farming with MR
- 2. Virtual Training for Farmers
- 3. Remote Assistance and Collaboration
- 4. Crop Scouting and Pest Management
- 5. Livestock Management
- 6. Smart Greenhouses
- 7. MR-Enabled Farm Machinery
- 8. Drone Monitoring and Data Visualization
- 9. Water Management and Irrigation
- 10. Climate Change Adaptation
- 11. Virtual Farm Tours
- 12. Farm Planning and Design
- 13. Supply Chain Transparency
- 14. Agricultural Research and Development
- 15. Gamification and Community Engagement
- Conclusion
Mixed reality (MR) blends virtual reality and augmented reality technologies to create immersive experiences that overlay digital content onto the physical world. This innovative technology is revolutionizing the agricultural industry by improving productivity, decision-making, and sustainability. In this blog post, we will explore 15 real-world examples of how mixed reality is being utilized to transform agriculture.
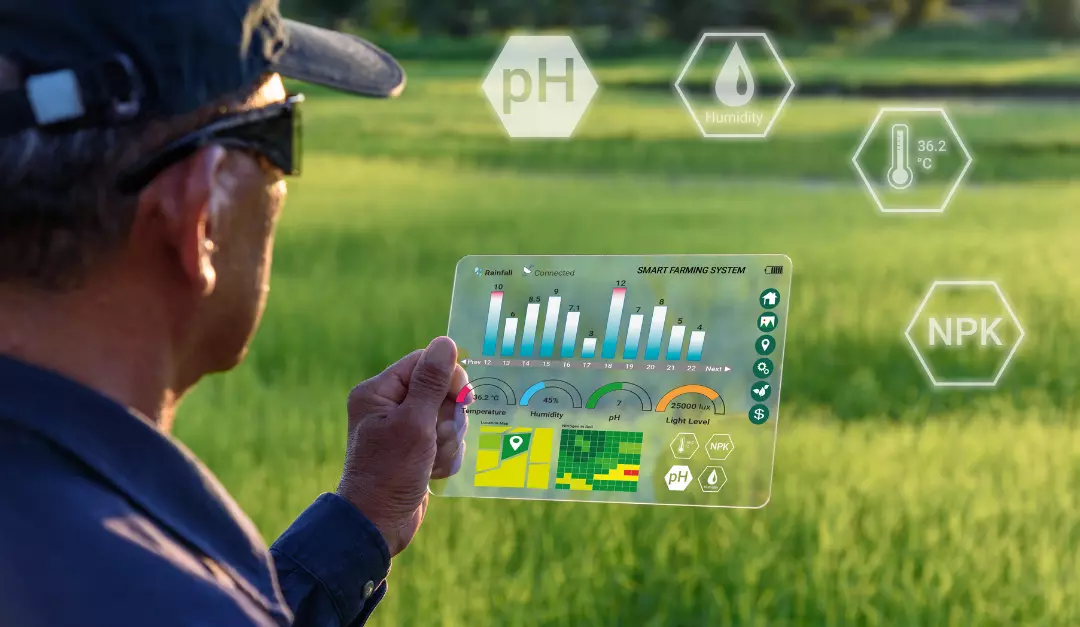
1. Precision Farming with MR
John Deere, a leading agricultural equipment manufacturer, has developed an MR application to help farmers visualize real-time data on soil conditions, crop health, and weather. By integrating with sensors and GPS systems, farmers can access precise information about soil moisture, nutrient management, and yield prediction, which can improve decision-making and resource utilization.
2. Virtual Training for Farmers
HoloLens, Microsoft’s MR headset, has been used to create immersive and interactive training programs for farmers. By simulating various farming scenarios and providing hands-on learning experiences, MR can help farmers gain knowledge and improve their skills more effectively than traditional training methods.
3. Remote Assistance and Collaboration
Companies like XMReality offer remote guidance solutions that enable agricultural experts to virtually assist farmers in diagnosing crop issues or equipment malfunctions. Using MR, experts can overlay digital instructions onto the physical environment, helping farmers to quickly resolve problems and increase efficiency.
4. Crop Scouting and Pest Management
Ceres Imaging, an agricultural analytics company, has developed an MR application that helps farmers identify pests and diseases in real-time using image recognition technology. By integrating with drone-collected data, farmers can deploy targeted and effective pest control measures, reducing chemical usage and crop loss.
5. Livestock Management
Microsoft’s FarmBeats project has explored the use of MR for monitoring livestock health, tracking movement, and managing breeding programs. With real-time data analysis, farmers can make better decisions about animal welfare and productivity, ultimately improving the profitability of their operations.
6. Smart Greenhouses
Companies like Heliospectra have developed MR-enabled solutions for smart greenhouses, allowing farmers to monitor and adjust factors such as temperature, humidity, and light. With MR, farmers can optimize greenhouse conditions, leading to reduced resource usage and increased yield.
7. MR-Enabled Farm Machinery
CNH Industrial, a global leader in agricultural machinery, has showcased MR concepts for controlling and monitoring farm machinery. With MR, farmers can access real-time performance data, reducing labor costs and improving productivity.
8. Drone Monitoring and Data Visualization
Parrot, a leading drone manufacturer, has partnered with Pix4D to create an MR application that visualizes drone-collected data, such as crop health and growth patterns. By overlaying this information onto the physical environment, farmers can make more informed decisions about crop management and resource allocation.
9. Water Management and Irrigation
Israel-based company Netafim has developed an MR application that helps farmers visualize and manage water resources more effectively. By integrating with irrigation systems and soil sensors, farmers can monitor water usage and ensure optimal irrigation schedules, reducing water waste and improving crop yields.
10. Climate Change Adaptation
The CGIAR Platform for Big Data in Agriculture has been researching the use of MR to help farmers prepare for and adapt to the effects of climate change. By simulating extreme weather events and shifting growing seasons, MR can contribute to increased resiliency and sustainability in agriculture.
11. Virtual Farm Tours
Bayer Crop Science has created immersive virtual tours of farms using MR technology, allowing people to experience agriculture in a new way. These tours have the potential to benefit education, tourism, and marketing efforts while raising awareness about sustainable farming practices.
12. Farm Planning and Design
Trimble, a leading provider of geospatial solutions, has developed an MR application that allows farmers to create 3D farm models and experiment with different layouts and designs. By visualizing their farms in a virtual environment, farmers can optimize land usage, infrastructure, and crop placement, leading to more efficient and sustainable farm operations.
13. Supply Chain Transparency
IBM’s Food Trust platform utilizes MR to track and visualize the journey of agricultural products from farm to table. By providing detailed information on the origin, processing, and transportation of food items, MR can help improve supply chain transparency and consumer trust in the products they consume.
14. Agricultural Research and Development
The University of Illinois has been using MR to simulate and test new agricultural technologies and practices in a virtual environment. This approach can lead to faster and more effective innovation in the industry, as researchers can identify potential issues and optimize solutions before implementing them in real-world scenarios.
15. Gamification and Community Engagement
FarmAR, an MR application, gamifies the farming experience by overlaying interactive content onto the physical environment. Users can learn about sustainable farming practices, engage with local food systems, and connect with the farming community. This not only educates consumers but also fosters a deeper appreciation for agriculture and the challenges farmers face.
Conclusion
Mixed reality holds enormous potential in revolutionizing the agricultural industry. By enhancing productivity, decision-making, and sustainability, MR technologies can play a critical role in addressing global challenges such as population growth, food security, and climate change. Continued research and investment in MR applications are essential for harnessing the full potential of this groundbreaking technology and ensuring a more sustainable and prosperous future for the world’s agricultural sector.